Anycast: The Internet's Traffic Distribution Powerhouse
🌐 Understanding Anycast: How It Works and Why It Matters
In the modern internet, speed, reliability, and scalability are essential. Anycast is a powerful network routing technique that helps deliver exactly that—by enabling the same IP address to be used by multiple servers across the globe.
🔄 What Is Anycast?
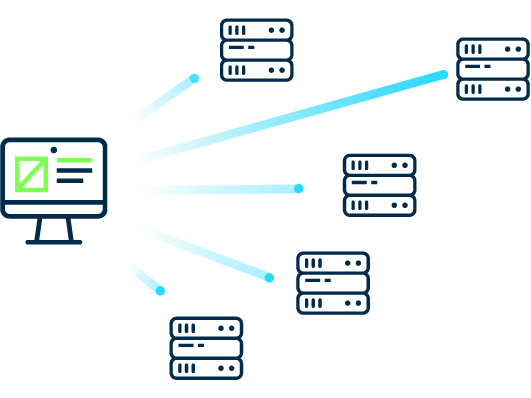
Anycast is a routing method where multiple servers share the same IP address, and traffic is routed to the nearest or best-performing server. Instead of connecting to one fixed destination, users are automatically connected to the most optimal server, based on factors like:
Geographic proximity
Network latency
Routing efficiency
Server availability
Unlike Unicast, which maps one IP to one server, or Multicast, which targets multiple receivers, Anycast creates a "one-to-nearest" routing model.
⚙️ How Anycast Works
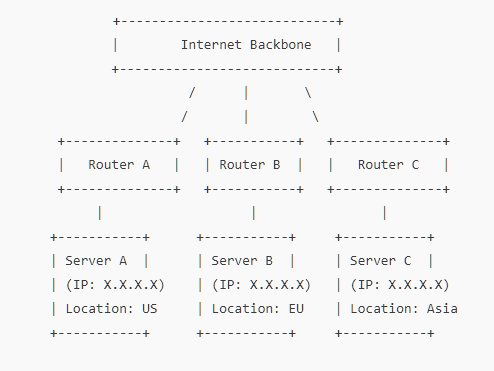
Same IP on Multiple Servers: Several servers (often in different locations) are configured with the same IP address.
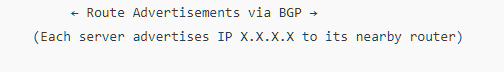
BGP Route Advertisement: Each server advertises this shared IP using BGP (Border Gateway Protocol) to nearby routers.
Routing to the Nearest Server: Routers on the Internet determine the shortest or lowest-latency path to that IP. Requests are routed to the "nearest" server from the network’s point of view.
Failover and Load Distribution: If one server goes offline, traffic is automatically rerouted to the next nearest healthy server.
✅ Why Anycast Is Important
High Availability: Automatically redirects traffic during server failures without user interruption.
Low Latency: Users are connected to the closest data center or edge server.
Improved Load Balancing: Traffic is naturally distributed across servers.
DDoS Mitigation: Spreads attack traffic, reducing impact on individual servers.
Scalability: Add new servers under the same IP easily as demand grows.
📦 Real-World Use Cases
🔹 AWS Route 53
Amazon’s Route 53 DNS service uses Anycast to ensure fast DNS resolution globally. When a user queries a domain, their request is routed to the nearest DNS server—improving speed and fault tolerance.
🔹 Global DNS Infrastructure
Most root DNS servers and TLD (Top-Level Domain) servers use Anycast. For example:
Root Servers like F, J, K are hosted using Anycast across hundreds of locations worldwide.
TLD servers for .com, .net, and others ensure global reliability and fast DNS lookups using Anycast.
🔹 CDNs (Content Delivery Networks)
Companies like Cloudflare, Akamai, and Fastly use Anycast to deliver cached web content from the nearest edge server to users.
💡 Anycast for Small Companies
You don’t have to be a big cloud provider to benefit from Anycast. Smaller businesses can use services that support Anycast to improve performance and resilience:
Third-party DNS providers (like Cloudflare, Google DNS, or Route 53) offer Anycast-powered DNS out-of-the-box.
CDN services with Anycast distribution help small websites scale globally with faster content delivery.
Email or VPN gateways: A distributed Anycast setup for access points can improve connectivity and availability.
Even without running your own Anycast infrastructure, leveraging existing platforms allows small companies to tap into global performance and reliability gains at minimal cost.
📌 Conclusion
Anycast is a foundational part of how the modern internet achieves high performance and fault tolerance. Whether you’re running a global DNS service or a small business website, Anycast can help deliver faster, more reliable, and scalable user experiences—with minimal complexity.